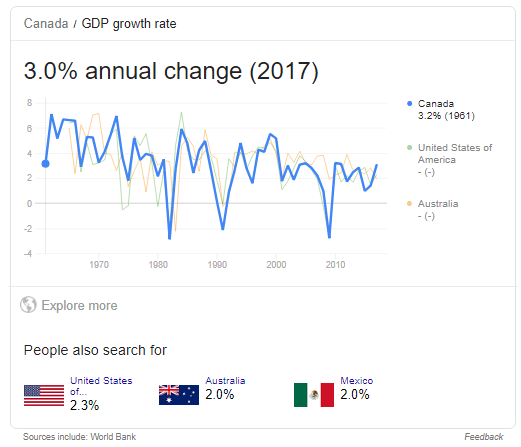
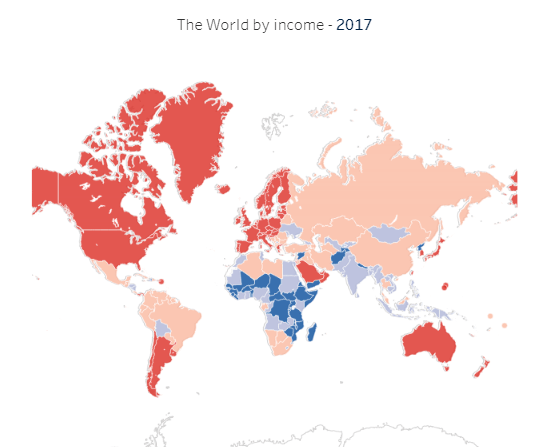
Law 30: 02 Why we Need Laws
Some links and resources posted here that go along with our section.
- Watch the Without Rule of Law video (below) – open it in YouTube to play it and watch to 16 minutes worth.
- Personal Inquiry Search: Select one of the two following options and develop a personal summary – either in written form (half page typed) or an audio reflection (4 minutes min) – of what you have or can learn from the topic selected.
- Research to learn whether Venezuela has Rule of Law right now and if not what is causing WROL (without rule of law). Consider, too, how long the situation there has been escalating – long term or mostly recent? Was there a specific trigger that’s changed things?
- Explore the World Justice Project Rule of Law Index 2017-2018 and read the Report Highlights. You can search certain country pages (Canada vs Denmark or U.S.A) to see how they’re rated differently. Develop a personal summary of your findings/what you can learn from the site.
- Viewing Activity: “You Should Have Stayed Home” Fifth Estate documentary on police use of force during 2010 G20 Summit in Toronto. Even countries with high Rule of Law function can fall victim to moments of WROL. Watch and take notes of significant details or comments you’d like to make to add to the discussion.
- Cultural Relativity: Articles referenced in the discussion on the burka, legal, required, and considered Just in some countries, while banned in others.